Business Research Proposal Sample: The Impact of AI on Business Performance in India
- 18 November 2024
- Posted by: OAH
- Category: Business & Management

This is a business research proposal sample work that examines how AI affects Indian companies’ performance. It focuses on how AI deployment affects organizational effectiveness and employee attitudes at major firms like Infosys, Tata Technologies, and HCL. The study is a useful tool for professionals and research enthusiasts because it provides insights into AI-driven initiatives through theoretical models and statistical methods. This sample research proposal will also help better understand how to write a research proposal that your professor can approve for a dissertation.
Do you also need Online Assignment Help? Contact us!
BUSINESS RESEARCH PROPOSAL SAMPLE WORK
THE IMPACT OF AI ON BUSINESS PERFORMANCE IN INDIA FROM THE EMPLOYEES’ PERSPECTIVE
Table of Contents
Abstract
This research proposal aims to analyze the effect of AI on business performance from the employees’ end in Indian organizations. AI, the independent variable is made up of machine learning, natural language processing, robotics, and neural networks. The dependent variable business performance is captured by factors such as; productivity efficiency and over organizational performance.
The objectives of this study are threefold: in order to understand the impressions of the personnel concerning the effects of AI on performance, to establish the dependencies of different forms of AI on the willingness of the employees to adopt AI, and to assess the factors influencing either the acceptance or rejection of the application of artificial intelligence. Sources of data for this research are secondary quantitative data such as annual reports, insider studies, and employee questionnaires of four leading Indian companies namely HCL, Tata Technologies, Wipro and Infosys for the last four years.
In fact, the research design will be conclusive, and in the case study, the researcher will be using descriptive statistics, regression analysis, and correlation analysis with the help of tools of Microsoft Excel and SPSS to analyze data. Expected outcomes include: These include understanding of the various perceptions employees have on the impact of AI in business and map the key perceptions along with key drivers for positive and negative perceptions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is now an integral part of contemporary technologies and development, implementing itself into different areas of business all over the globe. The AI market size in India has been growing and got up to 4.1 billion U.S. dollars, with machine learning being the largest component at 2.7 billion dollars.
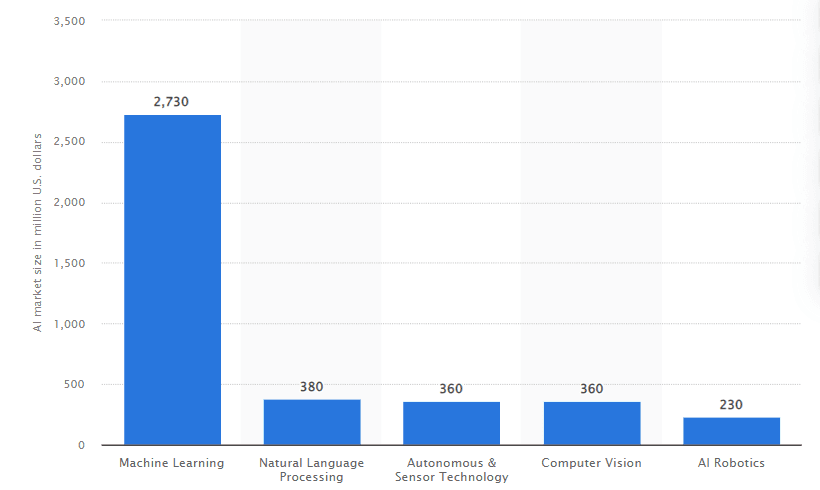
Figure 1.1: India’s Artificial Intelligence Market (2023)
(Source: Statista, 2024)
As per Jaiswal et al. (2023), Such a massive increase proves AI as a strategic agent of efficiency by optimizing and streamlining business processes, making it a vital element of Industry 4.0. Hence, as organizations integrate AI technologies in their operations, the IT industry in India that employs a large chunk of the global IT workforce will continue to grow. India started with ‘Tata Consultancy Services’ in the context of IT in 1967 and currently plays a key role in IT services, consulting, and outsourcing for more than 19% of the total global IT spending by 2021. This has placed India as a key player within the IT outsourcing services all while nurturing AI and IoT through governmental support and foreign investment. AI technologies feature multiple domains such as machine learning, robotics, artificial neural networks, and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Machine learning AI is the largest branch of AI and involves the use of software that helps analyze data and use the data obtained from the analysis to predict other data or use it to apply the knowledge that it has gained from the other data (Fu et al., 2023). Robotics, another broad major, deals with designing and programming robots for various purposes like self-driving cars.
1.2 Importance
For several reasons, it is imperative to learn about the effects of AI on business performance from the employees. First of all, it is important to mention that employees are the primary users and champions of AI solutions within enterprises. Quite evidently, their experiences, perceptions, and attitudes bear the brunt in the success or failure of AI integration. More specifically, the growing presence of AI in the Indian business environment, together with technology and culture, renders such insights valuable (Malik et al. 2023). Some of the top Indian organizations involved in implementing AI are Tata Technologies, Infosys, Wipro, and HCL are the organizations are pioneers in AI implementation and setting standards for the application of new innovation to business operations. For instance, Tata Technologies has been exploring AI to improve product development and engineering services which has changed the dynamics of most of its workforce and business. Infosys, yet another tech MNC’s, also incorporates the use of AI to enhance customer experiences as well as operations, which ensures that employees work in conditions that are dynamic and require the integration of optimum innovative technologies frequently. The implementation of HOLMES by Wipro to encode routine tasks is an example of how the development of AI can impact conventional business activities, which demand changes in employment skills and intelligence (Thewealthmosaic, 2024).
Secondly, knowledge from employee studies offers insights into the prospects and issues of AI implementation in the workplace. Such findings can help organizations design effective plans to deploy AI in a way that meets the expectations of its users and that would ultimately improve the organizational performance (Chen et al., 2021). For example, Infosys has recently established training courses to prepare its workforce for AI, as it understands that this is an essential factor for leveraging AI. Likewise, the corporate strategy of Wipro to reskill its employees underlines that organizational AI management needs to consider the existing and potential abilities of employees.
1.3 Problem Statement
Amidst the growing trend of scholars focusing on the driver of AI for business performance, there are apparently few investigations relating to the employees’ experience of AI, especially in the Indian context. Less attention has been paid to the human factor when adopting AI despite the fact that most AI projects revolve around it (Boustani, 2022). This research will try and fill this gap by offering an overall view of how employees have embraced AI and what they think it has done to business performance in India.
1.4 Research Questions
- What are the perceptions of employees in India regarding the impact of AI on business performance?
- How do different AI technologies (e.g., machine learning, NLP, robotics) influence employees’ attitudes toward AI adoption in the workplace?
- What are the key factors that affect employees’ acceptance or resistance to AI integration in Indian businesses?
1.5 Aim and Objectives
Aim
The aim of this research is to analyze the impact of AI on business performance in India from the employees’ perspective using secondary data sources.
Objectives
- To analyze employees’ perceptions of AI’s impact on business performance in India.
- To identify the influence of various AI technologies on employees’ attitudes towards AI adoption.
- To evaluate the key factors that affect employees’ acceptance or resistance to AI integration in Indian businesses.
1.6 Significance of the Study
This study will be useful in enhancing the existing academic knowledge through filling a gap that has not been covered when employees view the effect of AI on business performance. The literature review has also elicited the absence of scholarship that addresses how employees make sense of AI adoption in their workplace, or the human angle of AI technology (Fu et al. 2023). The research will contribute a part of the broad knowledge by presenting data derived from employees’ survey of their attitudes towards AI, perceiving benefits, and risks and their influence on organizational performance. For companies, the insights into how their employees perceive and interact with AI increases the potential for designing better approach for the integration of AI in organizations. Thus, in aggregate with the needs and expectations of employees, AI can improve job satisfaction and delivery quality, and, in consequence, business performance (Basri, 2020).
2. Literature Review
2.1 Global Studies on AI’s Impact on Business Performance (IV: Artificial Intelligence; DV: Business Performance)
2.1.1 Overview of AI Technologies and Business Applications
AI can be defined as a complex science and technology domain including machine learning, NLP, robotics, and neural networks. AI is based on algorithms that are capable of learning from data and making forecasts. NLP is an interdisciplinary subfield that deals with the interaction between computers and human language, with a view to processing natural languages. According to Abrokwah-Larbi, and Awuku-Larbi (2024), Robotics is defined as the creation, establishment, and utilization of robots while neural networks are computing systems modeled after the biological neural networks that make up the brains of animals. In general, the usage of artificial intelligence has enhanced business processes all across the globe. According to Basri (2020), Predictive analytics is the use of artificial intelligence to forecast the future using past event data to facilitate strategic decision-making.
2.1.2 Key Findings from Global Research
It appears from studies that AI has a deep effect on business outcomes. AI improves the use of automation technology as companies avoid the compromise of quality as they expand their operations. These insights help boost productivity because AI can predict exactly where and how resources and operations should be devoted to minimizing inefficiency. Innovation is another important advantage, as AI contributes to the growth of new solutions and products, which provide competitive advantages on the market. AI success stories from great multinational companies prove the importance of using AI (Chatterjee et al. 2020).
2.2 Indian-specific Studies on AI’s Impact on Business Performance
According to Bhardwaj et al. (2020), the use and implementation of AI solutions have been growing steadily in India in the recent past. The Indian government has launched several schemes and policies for the AI adoption because it believes that AI has the potential to foster innovation and economic growth in the country. For example, with the Indian National AI Strategy, India intends to become one of the leaders by developing AI research and development, encouraging AI education, and AI venture.
2.2.1 Case Studies of AI Implementation in Indian Companies
Tata Technologies
At Tata Technologies they use artificial intelligence in product development and in engineering services. With AI being incorporated in the design and production line, it has made it possible for the company to create new products and execute its business at optimum levels (Rana et al., 2022).
Infosys
AI is utilized at Infosys to enhance the value proposition, as well as customer satisfaction and business processes. The use of artificial intelligence in the company’s products involves result interpretation for improving the relationship with customers and increasing consumer loyalty.
Wipro
In the case of Wipro, an example of how organizations have applied AI is through HOLMES – a platform that is aimed at automating repetitive tasks. HOLMES uses machine learning and NLP to integrate and streamline tasks, for example, data input, customer service, compliance oversight, and more (Budhwar et al. 2022).
HCL
The DRYiCE suite that is offered by HCL is able to use Artificial intelligence to automate the business processes. With the use of AI and Robotics, DRYiCE optimizes the amount of work that goes into tasks like IT operation, service management, and business operations thereby lowering costs and improving service quality.
2.3 Employee Perspective
2.3.1 General Attitudes and Perceptions
Cross-cultural research shows that employees hold different attitudes toward AI. Some of the employees have positive attitudes towards AI and recognize the benefits it brings like Working smart, reducing Working load, and enhancing efficiency among others while some have negative attitude towards AI like the fact that AI will take over our jobs and the need to learn new skills among others. Clearly, the changes, that AI has brought to job content, employee satisfaction, and skills needed, are quite profound, as people have to adjust to new technological conditions (Soni et al., 2020).
2.3.2 Case Studies and Surveys
Examples of surveys and case studies from companies, including IBM and Google, increase awareness of employee concerns and emphasize that addressing them and facilitating AI acceptance are critical approaches for businesses. These firms have introduced talent development plans to prepare employees to engage with the emerging Artificial Intelligence systems. These companies have enhanced employee engagement and effectiveness by working with them to adopt AI properly and responding to their concerns (Dwivedi et al. 2021).
2.3.3 Indian-specific Studies on Employee Attitudes Towards AI
Employee Perceptions in Indian Companies
Research conducted in India towards the acceptance of AI shows that employees acknowledge the advantages but have issues with the usage of these technologies. Research studies indicate that employees embrace the role that AI could play in improving working output and productivity but worry about displacement and requirements for constant skills updates.
Case Studies of Employee Experiences in Indian Companies
Tata Technologies
Tata Technologies company has encouraged and instituted training and development programs to enhance the use of artificial intelligence. These programs are intended to provide the employees with competencies that would enable them to handle AI technologies within workplaces to ensure high levels of productivity and satisfaction. According to Laxmi and Leela. (2023), by implementing a CPL strategy, Tata Technologies makes a point of ensuring that its human capital is always set to meet the market competition.
Infosys
Infosys has implemented several training programs that can assist the workers in AI integration into various processes. Such programs include the training in the field of artificial intelligence technologies, conducts workshops and certification. Thus, with regard to Infosys, investments in staff development are made with the ultimate goal of offering proficiency in AI to enhance business outcomes.
Wipro
Wipro continues to organize training activities aimed at bringing employees up to speed on the incorporation of artificial intelligence in the workplace. The company provides continuing education in artificial intelligence and other technologies, thus enabling enhance workforce competence to fit new requirements of their positions.
HCL
HCL has promised to address the issues employees may have with AI by taking certain steps to ensure easy implementation. The company also offers resources that are used to train and educate its employees on how to work with AI technologies and this is done frequently (Sharma and Saxena, 2024). In this way, HCL decided to address these concerns of employees and customers to establish a desired work culture and optimize organizational functioning.
2.4 Gaps and Contributions
2.4.1 Identifying Gaps in the Current Literature
However, as more research is conducted on the topic of AI in the workplace, there is still a significant absence of studies on the employees’ side of things when it comes to AI adoption in the Indian context. Quite a number of analyses focus on technological and economic factors but there is little attention given to human factors.
2.4.2 Contributions of This Study
As a result, this study intends to assess the degree of employees’ awareness concerning the effects of AI on organizational performance in Indian organizations. By examining the phenomenon from the employees’ perspective, the study will complement existing literature in the following ways. This research, relying on secondary data, will provide an extensive perspective on how AI influences business outcomes from the employees’ viewpoint.
2.5 Theoretical Framework
2.5.1 Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
The most frequently used model that addresses how users adopt and integrate technology is called the Technology Acceptance Model. TAM posits that two main factors determine technology acceptance: One is perceived usefulness and the other is perceived ease of use.
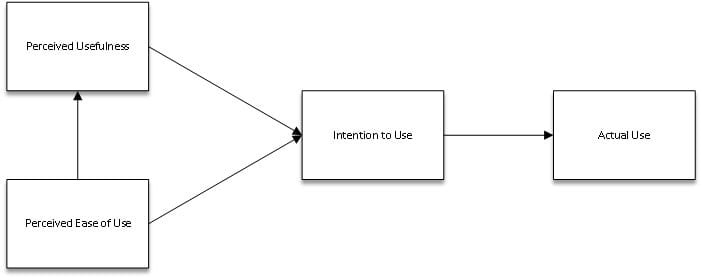
Figure 4.1.1: Technology Acceptance Model
(Source: Open.ncl.ac.uk. 2024)
In other words, perceived usefulness is the extent to which the user views that the use of a particular system will improve their performance on the job while perceived ease of use is the extent to which the user perceives that the use of the system is trouble-free (Kamal et al. 2020). TAM can further assist in understanding how AI is perceived in business particularly by employees due to the perceived usefulness and ease of use.
TAM will be employed to analyze employees’ reactions toward the implementation of AI. Thus, based on the perceived usefulness and ease of use of AI technologies among employees, this study can determine the factors that impede or promote acceptance and resistance to such technologies. Understanding these factors will assist businesses in aligning their AI implementation plans to counter these issues that inhibit its proper integration and improve overall worker satisfaction at the workplace. For example, if the study shows that employees have a positive attitude toward AI but reported it as costly to use, then organizations may develop strategies to enhance the training processes and develop effective interfaces.
2.5.2 Change Management Theory
This paper focuses on Change Management Theory, especially Kurt Lewin’s model, as a key approach to helping organizations respond to the need to manage change processes and how to incorporate new technologies such as AI into organizations. Lewin’s model includes three stages: These can be categorized into the three stages which include unfreezing, changing and refreezing. Unfreezing is about readjusting the attitude of the organization and making it ready for change, changing is the act of installing the new technology, and refreezing is the action that makes the change permanent and institutionalized within the organization (Armstrong 2019).
In the case of applying Change Management Theory to explain how organizations can support their employees in AI adoption, the following understandings will be considered. Finally, the research will identify the practices used by companies such as HCL, Tata Technologies, Wipro, Infosys and its subsidiaries, HCL Technologies, Tech Mahindra, Cognizant Technology Solutions, Capgemini, IBM, Oracle, SAP, Deloitte Consulting, Accenture, Ernst & Young (EY), KPMG, PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers), Atos, Fujitsu, NTT Data, CGI Group, DXC Technology, Mindtree, L&T Infotech, Virtusa, Hexaware Technologies, Syntel (now part of Atos), Zensar Technologies, Polaris Consulting & Services, Mphasis, Nagarro, SoftServe, Itron, Appirio, and Unisys in the three-stage process of unfreezing, change and refreezing. These findings will serve to give an understanding of what measures can be taken with the aim of preventing resistance and promoting change acceptance.
3. Research Methodology
3.1 Research Design
The study has a conclusive type of research design that is appropriate when the study is aiming at answering research questions and testing hypotheses. This design is suitable for this research, as it seeks to conclusively determine the effects of Artificial Intelligence on business outcomes from the employee lens in India (Research-methodology.net, 2024). The research can use secondary quantitative data will provide an interpretive analysis of extensive data sets to make unequivocal conclusions regarding the AI technologies and their impact on business results and employees’ attitudes.
3.2 Data Sources
The research shall employ secondary data acquired from four leading Indian enterprises, including HCL, Tata Technologies, Wipro, Infosys and its subsidiaries, HCL Technologies, Tech Mahindra, Cognizant Technology Solutions, Capgemini, IBM, Oracle, SAP, Deloitte Consulting, Accenture, Ernst & Young (EY), KPMG, PwC (PricewaterhouseCoopers), Atos, Fujitsu, NTT Data, CGI Group, DXC Technology, Mindtree, L&T Infotech, Virtusa, Hexaware Technologies, Syntel (now part of Atos), Zensar Technologies, Polaris Consulting & Services, Mphasis, Nagarro, SoftServe, Itron, Appirio, and Unisys over the last four years. They have been implementing AI in their business operations and therefore possess vast information regarding the performance of AI and the attitudes of employees towards AI. The secondary data will encompass annual returns, internal articles that dissect the effects of AI, employee satisfaction questionnaires, and organizational performance figures after AI integration.
3.3 Data Collection and Analysis
Under data collection, it will be necessary to compile relevant quantitative data for the selected firms. Measures will be confined to objective performance indices that have an impact on business outcomes (Productivity rates, operational efficiency, and innovation) and self-reporting and organizational commitment data (Job satisfaction, perceived job security, perceived attitudes towards AI technology). Descriptive statistics will be used to present the findings about sampled employee data in terms of measures of central tendency, variability, and demographics. The correlation analysis between AI deployment and performance indicators will be conducted using the regression analysis method which will reveal strength and direction of the relationships. Correlation analysis will be employed with the aim of establishing the nature and strength of various relationship patterns between different variables associated with AI and employee outcomes based on different context of companies Data handling and analysis will be conducted using statistical tools, particularly Microsoft Excel. Excel will be used to collect data and complete or start an analysis of data.
3.4 Ethical Considerations
This research will pay high ethical standards especially while dealing with the secondary data. Despite the data being secondary and accessible to the public, sensitive consideration will need to be taken to ensure that all data used is disguised and summarized in a way that will not breach the Data Protection Act.
3.5 Limitations
However, it is essential to realize that this research has some limitations which include the following. First, the use of secondary source data restrains the researcher from having full control over the data quality and details of the collection methods initially used by the firms. The data might not be comprehensive and roll out all the aspects of employee insights, or it might be laden with bias from the data collection of the source material.
Reference List
Abrokwah-Larbi, K. and Awuku-Larbi, Y., 2024. The impact of artificial intelligence in marketing on the performance of business organizations: evidence from SMEs in an emerging economy. Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, 16(4), pp.1090-1117.
Aimagazine.com. 2021 The impact of AI on employees’ professional lives Available at https://aimagazine.com/ai-strategy/impact-ai-employees-professional-lives [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]
Basri, W., 2020. Examining the impact of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted social media marketing on the performance of small and medium enterprises: toward effective business management in the Saudi Arabian context. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 13(1), pp.142-152.
Bhardwaj, G., Singh, S.V. and Kumar, V., 2020, January. An empirical study of artificial intelligence and its impact on human resource functions. In 2020 International Conference on Computation, Automation and Knowledge Management (ICCAKM) (pp. 47-51). IEEE.
Boustani, N.M., 2022. Artificial intelligence impact on banks clients and employees in an Asian developing country. Journal of Asia Business Studies, 16(2), pp.267-278.
Budhwar, P., Malik, A., De Silva, M.T. and Thevisuthan, P., 2022. Artificial intelligence–challenges and opportunities for international HRM: a review and research agenda. The InTernaTIonal Journal of human resource managemenT, 33(6), pp.1065-1097.
Chatterjee, S., Nguyen, B., Ghosh, S.K., Bhattacharjee, K.K. and Chaudhuri, S., 2020. Adoption of artificial intelligence integrated CRM system: an empirical study of Indian organizations. The Bottom Line, 33(4), pp.359-375.
Chen, D., Esperança, J.P. and Wang, S., 2022. The impact of artificial intelligence on firm performance: an application of the resource-based view to e-commerce firms. Frontiers in Psychology, 13, p.884830.
Dwivedi, Y.K., Hughes, L., Ismagilova, E., Aarts, G., Coombs, C., Crick, T., Duan, Y., Dwivedi, R., Edwards, J., Eirug, A. and Galanos, V., 2021. Artificial Intelligence (AI): Multidisciplinary perspectives on emerging challenges, opportunities, and agenda for research, practice and policy. International journal of information management, 57, p.101994.
Fu, F., Zha, W. and Zhou, Q., 2023. The impact of enterprise digital capability on employee sustainable performance: From the perspective of employee learning. Sustainability, 15(17), p.12897.
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1298932/india-ai-market-size-by-industry/ [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]
Jaiswal, A., Arun, C.J. and Varma, A., 2023. Rebooting employees: Upskilling for artificial intelligence in multinational corporations. In Artificial Intelligence and International HRM (pp. 114-143). Routledge.
Kamal, S.A., Shafiq, M. and Kakria, P., 2020. Investigating acceptance of telemedicine services through an extended technology acceptance model (TAM). Technology in Society, 60, p.101212.
Laxmi M and Dr. Leela M H. (2023). A Study on Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employee’s Performance. European Economic Letters (EEL), 13(4)
Malik, A., Budhwar, P., Mohan, H. and NR, S., 2023. Employee experience–the missing link for engaging employees: Insights from an MNE’s AI‐based HR ecosystem. Human Resource Management, 62(1), pp.97-115.
Open.ncl.ac.uk. 2024 Technology Acceptance Model: A review Available at: https://open.ncl.ac.uk/theories/1/technology-acceptance-model/ [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]
Panenkov, A., Lukmanova, I., Kuzovleva, I. and Bredikhin, V., 2021. Methodology of the theory of change management in the implementation of digital transformation of construction: problems and prospects. In E3S web of conferences (Vol. 244, p. 05005). EDP Sciences.
Pwc.in. 2024 AI: Possibilities of transforming the workplace Accessed from: https://www.pwc.in/consulting/transformation-consulting/artificial-intelligence.html [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]
Rana, N.P., Chatterjee, S., Dwivedi, Y.K. and Akter, S., 2022. Understanding dark side of artificial intelligence (AI) integrated business analytics: assessing firm’s operational inefficiency and competitiveness. European Journal of Information Systems, 31(3), pp.364-387.
Rana, N.P., Chatterjee, S., Dwivedi, Y.K. and Akter, S., 2022. Understanding dark side of artificial intelligence (AI) integrated business analytics: assessing firm’s operational inefficiency and competitiveness. European Journal of Information Systems, 31(3), pp.364-387.
Research-methodology.net. 2024 Research Design Available at: https://research-methodology.net/research-methodology/research-design/// [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]
Sharma, S. and Saxena, P., 2024. Role of Emotional and Artificial Intelligence in Employee Performance: A Perspective from the Indian Service Industry. Abhigyan, 42(1), pp.43-56.
Soni, N., Sharma, E.K., Singh, N. and Kapoor, A., 2020. Artificial intelligence in business: from research and innovation to market deployment. Procedia Computer Science, 167, pp.2200-2210.
Statista.com 2024 Size of artificial intelligence market in India in 2023, by sector Available at:
Thewealthmosaic.com. 2024 Wipro HOLMES Available at: https://www.thewealthmosaic.com/vendors/wipro/wipro-holmestm// [Accessed on 17 July, 2024]










