SWOT and PESTLE Analysis of TESLA Company: Detailed and Informative
- 22 November 2024
- Posted by: OAH
- Category: Business plans

This is a detailed SWOT and PESTLE Analysis of Tesla Company equipped with the latest information. The post will help management students understand PESTEL and SWOT analysis for Tesla Motors.
It covers Tesla’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats through a comprehensive SWOT framework. The report also covers PESTLE analysis for Tesla, which examines the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors affecting the company. This analysis will help management, business strategy, and marketing students understand the practical application of SWOT and PESTEL/PESTLE analysis through real-world business scenarios, in this case: Tesla Motors.
Need Assignment Help Online from the Best Experts? Contact us today!
SWOT AND PESTLE ANALYSIS FOR TESLA COMPANY
Table of Contents
About Tesla Company
Tesla Inc. is an American electric vehicle (EV) and clean energy company founded in 2003 by engineers Martin Eberhard and Marc Tarpenning, with Elon Musk joining soon after as an investor and chairman (Tesla, 2024). Known for its innovative approach, Tesla revolutionized the automotive industry by focusing on electric cars, energy storage, and solar power. Its mission is to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy. Tesla’s notable achievements include the development of high-performance electric vehicles, the introduction of Autopilot technology, and expansion into energy solutions through SolarCity and the Powerwall. The company continues to disrupt both the automotive and renewable energy markets (Kissinger, 2024).
SWOT Analysis of Tesla Company
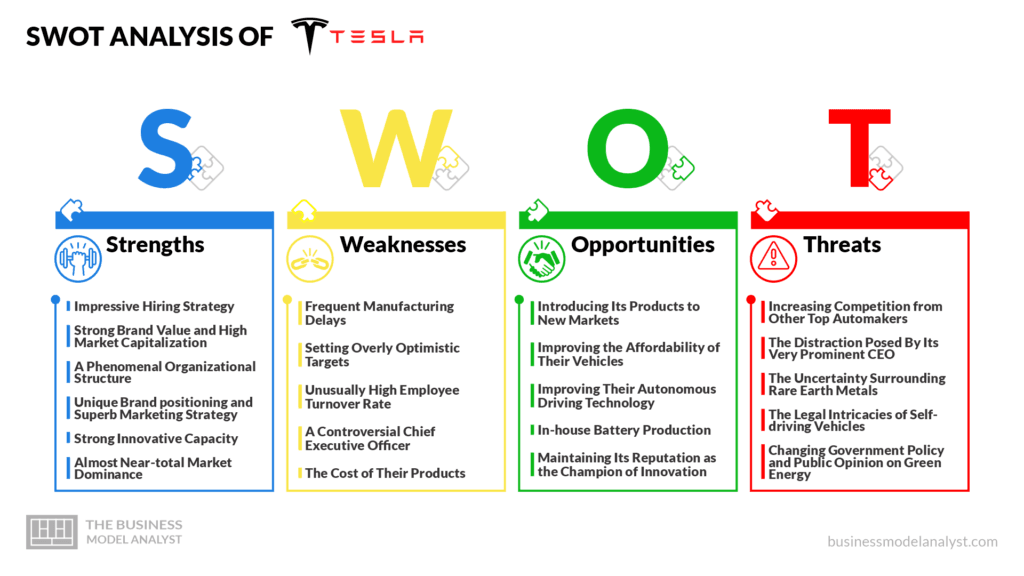
Strengths of Tesla Motors:
- Innovative Technology Leadership: Tesla remains at the forefront of the electric vehicle (EV) market, continuously advancing technology such as autonomous driving and long-range battery systems.
- Strong Brand Image: Tesla’s brand is synonymous with cutting-edge technology and sustainability, which helps attract loyal customers and enhance its market presence.
- Global Production Capacity Expansion: Tesla’s investment in Gigafactories worldwide increases production capacity and streamlines manufacturing processes, enabling faster scalability
- Vertical Integration: The company’s approach to vertical integration, especially in battery manufacturing and energy storage, strengthens its control over the supply chain and reduces dependence on external suppliers (Lino, 2024)
- Market Dominance in EVs: Tesla holds a significant share of the global EV market, benefiting from a growing consumer base focused on environmentally friendly alternatives
- Sustainability Commitment: Tesla’s commitment to sustainable energy solutions, including solar products and energy storage, enhances its appeal to eco-conscious consumers and bolsters its reputation as a clean energy leader.
This combination of technological leadership, brand strength, and sustainable practices gives Tesla a competitive edge in the rapidly evolving automotive and energy markets.
Also Read Impact of Brand Awareness on Consumer Behavior
Weaknesses of Tesla Motors:
- Production Capacity Constraints: Tesla struggles with limited production capacity, unable to meet growing global demand
- High Vehicle Prices: Tesla’s vehicles remain relatively expensive, limiting its market reach and customer base (Bhardwaj et al., 2020).
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: The company faces supply chain risks, especially concerning materials like lithium and cobalt
- Quality Control Issues: Some models, especially the Model 3, face inconsistencies in build quality.
- Limited Model Range: Tesla’s model offerings are limited, missing key segments like affordable EVs
- Dependence on CEO’s Image: Tesla’s heavy reliance on Elon Musk’s public persona may risk brand stability (Mahmud, 2023).
These weaknesses present challenges that Tesla must address to maintain its competitive advantage.
Opportunities for Tesla Motors:
- Global EV Market Expansion: Increasing global demand for electric vehicles presents significant growth opportunities for Tesla
- Affordable EV Models: Tesla can target broader markets by developing more affordable electric vehicles.
- Energy Storage Growth: The rising demand for renewable energy solutions offers growth in Tesla’s energy storage products
- Autonomous Driving Development: Advancements in self-driving technology could lead to new revenue streams, such as autonomous ride-sharing.
- New Market Penetration: Expanding operations in emerging markets, particularly in Asia and Africa, offers considerable growth potential (Ding and He, 2022)
- Sustainability Trends: Tesla can capitalize on the growing emphasis on sustainable energy, integrating products like solar roofs
These opportunities enable Tesla to diversify and strengthen its position in the global market.
Threats for Tesla Motors:
- Intensifying Competition: Established automakers and new entrants are increasing their electric vehicle offerings, intensifying competition.
- Regulatory Challenges: Tesla faces complex global regulations regarding emissions, safety standards, and autonomous driving
- Material Price Volatility: Fluctuating prices of key materials, such as lithium and cobalt, pose production cost challenges
- Supply Chain Risks: Disruptions in the supply chain, particularly for critical battery components, can impact production (Jiang, 2022)
- Legal and Safety Issues: Tesla’s autopilot and safety features face scrutiny, which could lead to legal risks
- Market Volatility: Economic downturns and market fluctuations may affect consumer demand for premium-priced electric vehicles.
These external threats require strategic adjustments for Tesla to maintain its market leadership.
PESTLE Analysis of Tesla Company

Political Factors:
- Government Regulations: Tesla must navigate a complex regulatory environment across different countries. Regulatory policies regarding emissions, safety standards, and vehicle manufacturing directly impact Tesla’s operations (Khan, 2021). Stricter emissions regulations in the European Union, for example, can benefit Tesla, while regulatory changes in the US regarding electric vehicle incentives could influence demand
- Trade Policies: Tariffs, import/export restrictions, and trade wars can significantly affect Tesla’s supply chain and market expansion. For instance, the ongoing US-China trade tensions have impacted Tesla’s operations in China, which is crucial for both production and market sales.
- Geopolitical Influences: Political instability, such as in Europe or parts of Asia, can affect Tesla’s ability to maintain its manufacturing footprint. Furthermore, shifting political climates regarding clean energy policies can either provide opportunities or impose challenges.
Economic Factors:
- Economic Conditions: Global economic conditions, including recessions or booms, affect consumer purchasing power. In downturns, Tesla may face reduced demand for its premium-priced electric vehicles, impacting sales.
- Currency Exchange: Tesla operates in multiple countries, and fluctuations in currency exchange rates can influence profits. A stronger US dollar, for example, can make Tesla’s products more expensive in foreign markets, potentially reducing demand.
- Market Demand: The increasing consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, such as electric vehicles, represents a significant economic opportunity for Tesla. However, changes in consumer preferences or increased competition from low-cost manufacturers may influence Tesla’s market share.
Social Factors:
- Consumer Preferences: Increasing awareness of environmental issues has driven consumer demand for electric vehicles (EVs), benefiting Tesla. As more consumers seek sustainable alternatives to traditional combustion engines, Tesla’s brand is well-positioned as an eco-friendly option. However, societal shifts toward lower-cost vehicles may challenge Tesla’s premium pricing strategy.
- Urbanization: With urban areas expanding, there is greater interest in compact, energy-efficient vehicles. Tesla’s range of vehicles, including smaller models like the Model 3, cater to these preferences, positioning the company well in urban environments where sustainability and practicality are key considerations (Ding and He, 2022)
- Cultural Factors: Tesla’s brand is often associated with innovation and luxury, appealing to affluent, tech-savvy consumers. However, as more competitors enter the EV market, Tesla must maintain its cultural cachet while broadening its appeal to mass-market consumers.
Technological Factors:
- Advancements in Battery Technology: Tesla continues to invest heavily in improving battery efficiency and reducing costs, which are crucial for the long-term viability of EVs. Innovations like the 4680-battery cell promise higher energy density and longer vehicle range, maintaining Tesla’s image of having the most advanced technology.
- Autonomous Driving: Tesla’s ongoing development of self-driving technology is a major focus. The company is working to refine its Autopilot and Full Self-Driving systems, aiming to revolutionize personal transport and introduce autonomous ride-sharing.
- Manufacturing Technologies: Tesla’s Gigafactories are equipped with cutting-edge manufacturing technologies that increase production efficiency and reduce costs. These technological advancements are crucial for scaling production to meet rising demand while maintaining quality (Ajitha and Nagra, 2021).
Legal Factors:
- Regulatory Changes: Tesla faces evolving global regulations regarding vehicle safety, emissions, and autonomous driving technologies. For example, stricter European emissions standards and regulations in China regarding EV manufacturing require Tesla to adapt its production processes and product offerings.
- Safety Standards: Tesla must comply with various safety regulations, including crash testing and self-driving vehicle safety. Any failures or issues in meeting these standards could result in legal liabilities, fines, or forced recalls, affecting the brand’s reputation.
- Intellectual Property: As Tesla continues to innovate in battery technology and self-driving software, it must protect its intellectual property from competitors and manage risks related to patents, trade secrets, and counterfeiting
Environmental Factors:
- Climate Change: As the world increasingly focuses on tackling climate change, Tesla’s clean energy solutions and electric vehicles align with global efforts to reduce carbon emissions. This creates growth opportunities, especially as more governments implement carbon reduction targets.
- Regulations: Tesla must adhere to various environmental regulations, including those surrounding waste management, battery recycling, and manufacturing processes. Compliance with these regulations is vital for maintaining the company’s sustainable image.
- Sustainability Efforts: Tesla has committed to sustainability through initiatives like solar power generation and energy storage solutions. This reinforces its brand as a leader in renewable energy, aligning with consumer expectations and regulatory incentives for sustainable companies (Dai, Li, and Pang, 2023).
References used for creating SWOT and PESTEL Analysis for Tesla Motors:
Ajitha, P.V. and Nagra, A., 2021. An overview of artificial intelligence in the automobile industry–a case study on Tesla cars. Solid State Technology, 64(2), pp.503-512.
Bhardwaj, S., Pandey, R., Sharma, S., Sejal, S., Iyer, G., Sharma, S., Ranjith, P.V. and Kulkarni, S., 2020. Problems faced by automobile industries: A case study on Tesla. International Journal of Tourism and Hospitality in Asia Pacific, 3(2), pp.78-88.
Dai, W., Li, Y. and Pang, Y., 2023. Innovation Model Analysis of New Energy Vehicles: Case Study of Tesla. Advances in Economics, Management, and Political Sciences, 29(1), pp.106-113.
Ding, J. and He, Y., 2022, April. Tesla Pricing Strategy Analysis: Take Model 3 a Example. In 2022 7th International Conference on Social Sciences and Economic Development (ICSSED 2022) (pp. 1010-1014). Atlantis Press.
Jiang, T., 2022, March. A business model to analyze the Tesla based on SWOT analysis and POCD. In 2022 7th International Conference on Financial Innovation and Economic Development (ICFIED 2022) (pp. 2896-2899). Atlantis Press.
Khan, M.R., 2021. A critical analysis of Elon Musk’s leadership in Tesla Motors. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, 11(1), pp.213-222.
Kissinger, D. 2024. Tesla SWOT Analysis & Recommendations. Available at: https://panmore.com/tesla-motors-inc-swot-analysis-recommendations#google_vignette [Accessed on 10.11.2024]
Lino, G. 2024. SWOT Analysis for Tesla Motors: A Comprehensive Guide. Available at: https://www.girolino.com/swot-analysis-for-tesla-motors-a-comprehensive-guide/ [Accessed on 10.11.2024]
Mahmud, S. 2023. Tesla SWOT Analysis 2024: In-Depth Report With Infographics. Available at: https://swotwizard.com/tesla-swot-analysis/ [Accessed on 10.11.2024]
Tesla, 2024. Tesla: Model Y. Available at: https://www.tesla.com/en_gb [Accessed on 10.11.2024]










